If you’re a veterinarian looking to deepen your understanding of administering intravenous solutions to animals, VetStarch is critical. To ensure that your treatment decisions are both knowledgeable and safe for the people receiving them, this article will provide an in-depth analysis of VetStarch’s prescribing information. Whether you’re a seasoned veteran or a rising star in the field, these guidelines will give you all the information necessary to use this product as a plasma substitute safely and effectively.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Indications and Usage Of VetStarc
VetStarch is an invaluable tool for treating and preventing hypovolemia in animals. Administered through intravenous infusion, this solution must be used with discretion, given that the patient’s blood loss, hemodynamics, and hemodilution effects play pivotal roles in determining the daily dosage and rate of infusion. However, caution should be exercised during the initial stages of the injection, as there is a risk of anaphylactoid reactions. In cases of dehydration, initiating treatment with a crystalloid solution is strongly recommended before VetStarch is introduced.
2. Dosage and Administration: The Heart of Medication Use
Adult Dose and Directions for Usage
Adult dosage is crucial and specific. It requires a nuanced understanding of the patient’s condition. Infusions must begin slowly to accommodate potential anaphylactoid reactions. To ensure a beneficial response, dosage adjustments might be necessary for patients with underlying cardiac or renal conditions, reflecting the need for careful observation and treatment planning.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
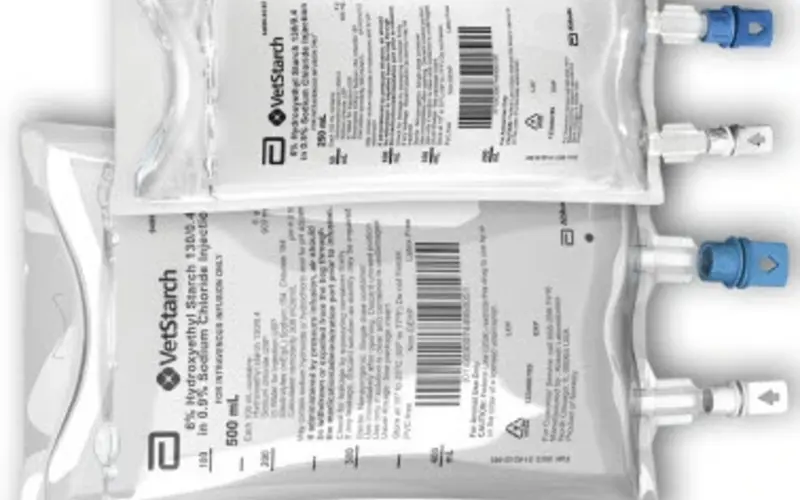
VetStarch is available in 250mL and 500mL flexible plastic intravenous containers. Each 100 contains 6g of hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 in isotonic sodium chloride solution. These options offer versatility in managing hypovolemia according to the scale of treatment required.
4. Avoiding Contraindications
Contraindications are the red flags that cannot be overlooked. If the patient has a known hypersensitivity to hydroxyethyl starch, existing fluid overload, renal failure unrelated to hypovolemia, or severe hypernatremia and hyperchloremia, VetStarch is not the solution. Conducting thorough patient history checks is vital to safeguard against these contraindications and prevent any complications.
5. Vigilance with Warnings and Precautions
The integrity of your treatment approach heavily relies on heeding the multitude of warnings and precautions associated with VetStarch.
Anaphylactoid and Hypersensitivity Reactions:
Irrational responses must be anticipated, with preparations to manage them promptly and effectively.
Fluid Overload:
Adjusting dosages for patients with heart or kidney disorders prevents this complication.
Dehydration:
A prior crystalloid solution mitigates the risk of exacerbating the condition with VetStarch.
Liver Disease and Bleeding Disorders:
Special care and monitoring of these patient groups are essential.
Kidney Function:
Regular monitoring is a must to preclude adverse renal effects.
Pancreatitis Diagnosis:
Elevated serum amylase from high dosages can obscure pancreatitis diagnosis.
Blood Component Dilution:
Higher doses can dilute vital blood components, necessitating careful dosage calculations.
6. Anticipating and Managing Adverse Reactions
Awareness of adverse reactions and their management is critical:
Pruritus:
A common side effect is requiring close observation.
Hemodilution:
It results in a decrease in hematocrit and the dilution of blood components. Regular bloodwork aids in monitoring these changes.
Reporting:
VetStarch manufacturers must be promptly informed of suspected adverse reactions for continuous product assessment.
7. Sensible Drug Interactions
While no interactions with other drugs or nutritional products are known, caution should still be exercised. Adding to the solution or co-administering with other compounds can lead to unpredictable interactions. It’s advisable only to blend VetStarch under the most controlled and informed circumstances.
8. Safe Usage in Special Populations
Understanding how your unique patient population interacts with VetStarch is a crucial part of responsible practice:
Renal Impairment:
Dosage adjustments are particularly pressing in patients with impaired renal function, ensuring that the benefits outweigh the risks.
9. Overdose Awareness
Though less common, overdose can occur, and a plan must be in place to manage it effectively. Monitoring closely and adjusting doses based on individual responses can prevent this.
10. Delving into the Description
Understanding the exact composition and characteristics of VetStarch is essential in making informed decisions about its application to patient care.
11. Clinical Pharmacology Unveiled
What underpins the effective use of VetStarch in clinical settings? This section uncovers the drug’s mechanism of action.
12. Navigating Nonclinical Toxicology
Assess the impact of VetStarch on various patient populations from a more comprehensive, nonclinical perspective.
13. Fostering References
A look at the research and data from studies that back up the prescribing information and uses of VetStarch.
14. The Findings in Practice
How is VetStarch stored, handled, and supplied? Practical considerations are laid out here.
By thoroughly understanding and applying this prescribing information, veterinarians can ensure the safe and effective use of VetStarch in their clinical practice. This listicle provides a deep dive into the complexities and critical considerations associated with this essential intravenous solution, aligning your practice with the highest standards of veterinary care.